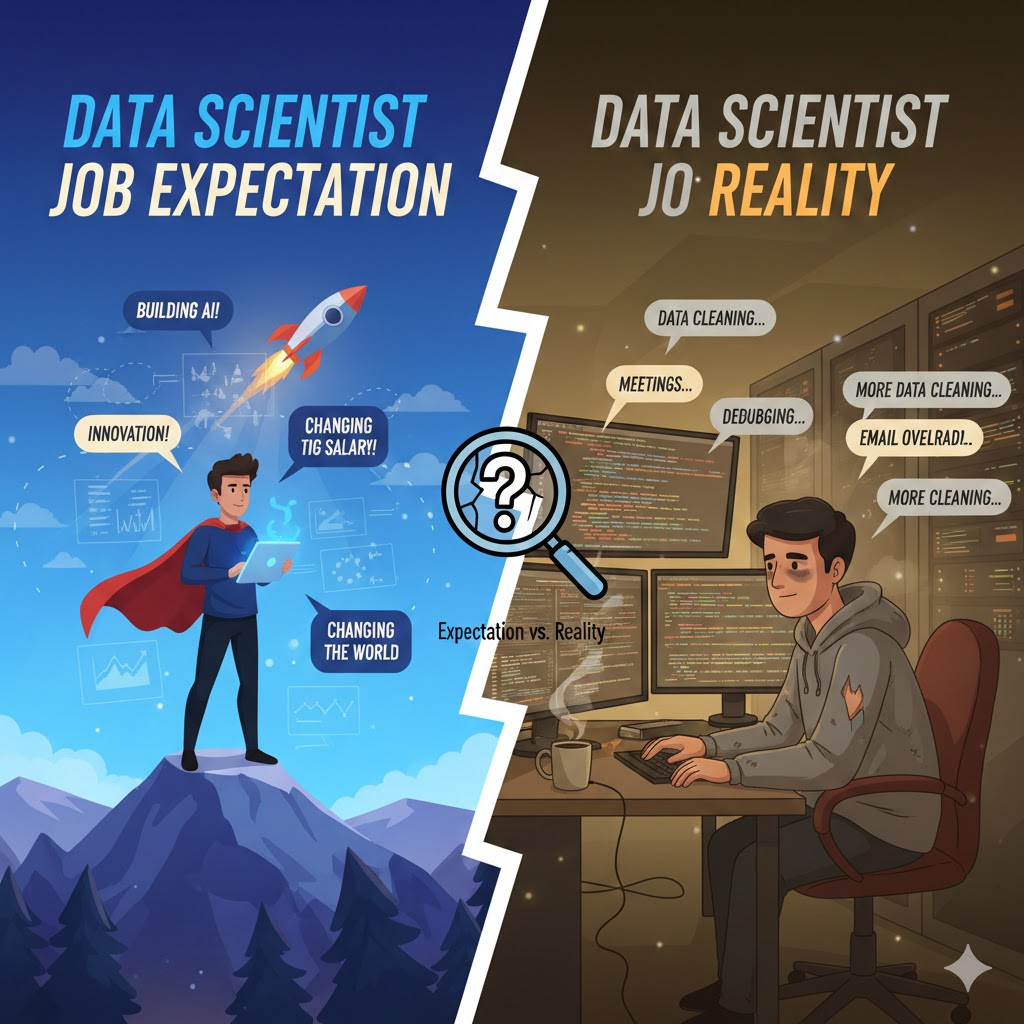
📊 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮 𝗦𝗰𝗶𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝘀𝘁 𝗝𝗼𝗯 𝗘𝘅𝗽𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝘃𝘀 𝗥𝗲𝗮𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆
Many people who want to be data scientists think that the job is largely about developing machine learning and deep learning models. The truth is that 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮 𝗦𝗰𝗶𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝘀𝘁 𝗝𝗼𝗯 𝗘𝘅𝗽𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝘃𝘀 𝗥𝗲𝗮𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆 is much more complicated than that, and knowing this early on might save you years of frustration.
In 2025–2026, data scientists will be expected to turn enormous amounts of raw data into useful business strategies by employing a mix of advanced statistical modeling, machine learning, and programming. More and more, companies want data scientists to do more than just construct models. They also want them to install, manage, and monitor these models in production, work with product teams, and explain their findings to people who aren’t technical.

Common Job Titles
- Data Scientist
- Machine Learning Engineer
- AI Specialist
- Data Analyst (with modeling focus)
Core Job Responsibilities
- Data Preparation & Engineering: Gathering, cleaning, and organizing large structured and unstructured datasets from various sources.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies to uncover hidden opportunities.
- Machine Learning Modeling: Designing, training, and optimizing predictive models and algorithms (e.g., classification, regression, clustering).
- Model Deployment (MLOps): Collaborating with engineers to put models into production and maintaining them.
- Strategic Communication: Translating complex technical findings into clear, actionable business insights for executives and stakeholders.
Technical skills are necessary.
1. Programming Languages: A strong command of R or Python is necessary.
2. Database querying: sophisticated SQL abilities for relational database management and manipulation.
3. Machine Learning Libraries: Knowledge of TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, or Scikit-learn.
4. Data visualization: Dashboard creation tools such as Tableau, Power BI, Matplotlib, or Seaborn.
5. Cloud Platforms: Knowledge of Azure, GCP, or AWS.
6. Big Data Technologies: It’s frequently necessary to have prior experience with Spark or Hadoop.
Soft Skills and Characteristics.
- Business acumen: Knowledge of how data initiatives complement organizational objectives.
- Curiosity and Problem-Solving: The desire to investigate information and resolve difficult, unclear issues.
- Communication: The capacity to use statistics to present a story to audiences who are not technical.
- Cooperation: Performing well in cross-functional teams (engineering, product).
Education and Experience
- Education: Typically a bachelor’s or master’s degree in computer science, data science, statistics, mathematics, or a related quantitative field.
- Experience:
- Entry-level: 0-2 years, with strong foundational knowledge and portfolio projects.
- Mid-level: 3-5 years, with experience in deploying models and independent project ownership.
- Senior-level: 5-7+ years, with experience leading projects, mentoring, and setting data strategy.
🔍 𝗘𝘅𝗽𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻
• ~65% of the time, machine learning
• About 25% Deep Learning
• About 10% of other tasks
This is a typical way of thinking because classes, tutorials, and social media all focus on algorithms and models.
🔍 𝗥𝗲𝗮𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆
A data scientist in the real world does a lot of important things every day:
• 20% Data Cleaning—Fixing problems with missing values, discrepancies, and data quality
• 15% Data Gathering—Getting information from different sources, APIs, and databases
• 15% Discussions and Meetings—Turning business concerns into data problems
• 12% Feature Engineering: This is often more important than choosing a model.
• 12–15% ML/DL—Building, tweaking, and testing models
• Maintenance, Documentation, and Other Tasks—Making sure that solutions are scalable, explainable, and reliable
Key Takeaways for Aspiring and Early-Career Data Scientists
• Knowing a lot of algorithms is not as important as having a strong data foundation.
• 𝗕𝘂𝘀𝗶𝗻𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝘂𝗻𝗱𝗲𝗿𝘀𝘁𝗮𝗻𝗱𝗶𝗻𝗴 & 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝘀𝗸𝗶𝗹𝗹𝘀 are needed
• Feature engineering and data quality often work better than complicated models
• Part of the work is making things, keeping an eye on them, and writing down what you do.
🚀 𝗖𝗮𝗿𝗲𝗲𝗿 𝗔𝗱𝘃𝗶𝗰𝗲
If you want to become a better data scientist:
• Spend time learning about 𝗱𝗮𝘁𝗮 𝘄𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗴𝗹𝗶𝗻𝗴, 𝗦𝗤𝗟, 𝗽𝘆𝘁𝗵𝗼𝗻, and 𝗘𝗗𝗔
• Get used to looking at problems from a business point of view
• Find out how to deploy and keep models up to date, not only train them.
Data science isn’t just about models; it’s about using faulty data to solve actual problems.
People frequently think that data science is mostly about constructing complex machine learning models, but in truth, a lot of it is about cleaning, wrangling, and establishing infrastructure (more than 60% of the job). To turn raw, unstructured data into useful information, you need more than just coding skills. You also need to be good at SQL, business communication, and managing stakeholders.
Important Differences: What you expect vs. what actually happens
Modeling and AI (80–90%): Many people expect to spend most of their time constructing, training, and improving complex neural networks and algorithms.
Reality: 60–80% of the effort goes into collecting, cleaning, and verifying the data. “Garbage in, garbage out” is a big worry since models are only as good as the data they use.
A Breakdown of Core Responsibilities in Reality
- Data Wrangling (20–25%): Getting rid of bad data, changing it, and dealing with missing numbers.
- SQL and Data Gathering (15–20%): Getting data from different APIs and databases.
- Company Problem Framing (15%): Turning company needs into data problems.
- Modeling and Optimization (10–15%): Making and tweaking algorithms.
- Maintenance and Deployment (10–15%): Monitoring the model’s performance and addressing issues related to data drift.
- Communication (10%+): Writing down and explaining findings to others who aren’t technical.
Common Mistakes and Truths
- What you think: You will use powerful AI every day.
- The truth is that simple SQL queries and rudimentary visualizations may typically solve 80% of business problems.
- Perception: Your data will be clean and well-organized.
- The truth is that data is typically untidy, unstructured, and poorly documented.
- The work is all about technology.
- In reality, data scientists often have to deal with stakeholders, manage expectations, and market their ideas.
Skills That Are Necessary in Real Life
Data scientists require more than just Python and tools like Scikit-learn or TensorFlow. They also need to be able to create stories with data, know a lot about the business domain, and be good at SQL.
The “Expectation vs. Reality” Skill Map
| Skill | What you thought you’d use | What you actually use |
| Math | Multivariable Calculus | Basic Statistics & Logic |
| Coding | Complex Algorithmic Design | df.dropna() and GROUP BY |
| AI | Large Language Models (LLMs) | If-Then Statements (Heuristics) |
| Tools | High-Performance GPU Clusters | Your laptop fan spinning very loudly |
Top 10 free AI courses from top universities