How do Search Engines really Work?
Search engines use a variety of complex algorithms and procedures to extract the most relevant information from large amounts of web content. Here is a breakdown of how they typically work:
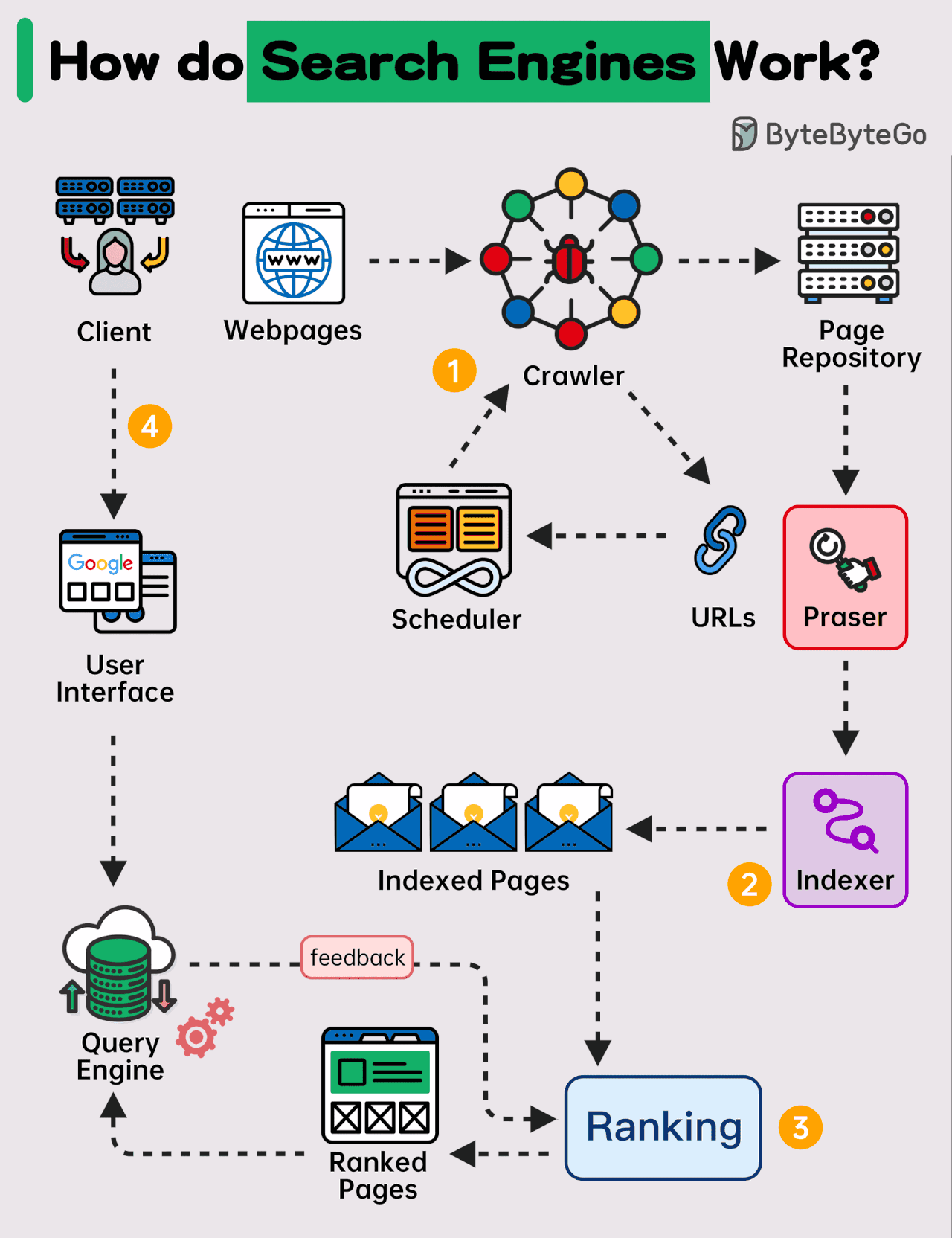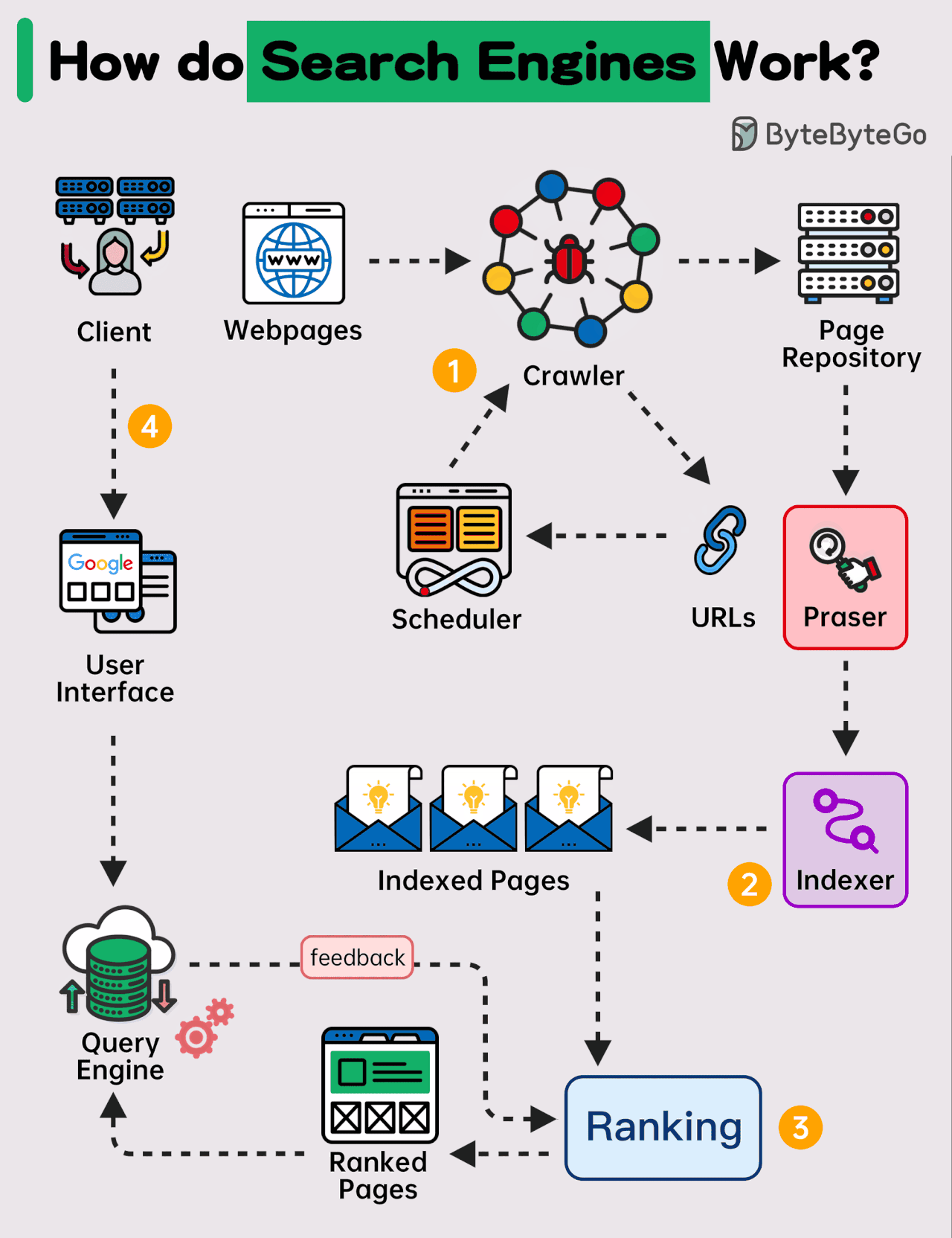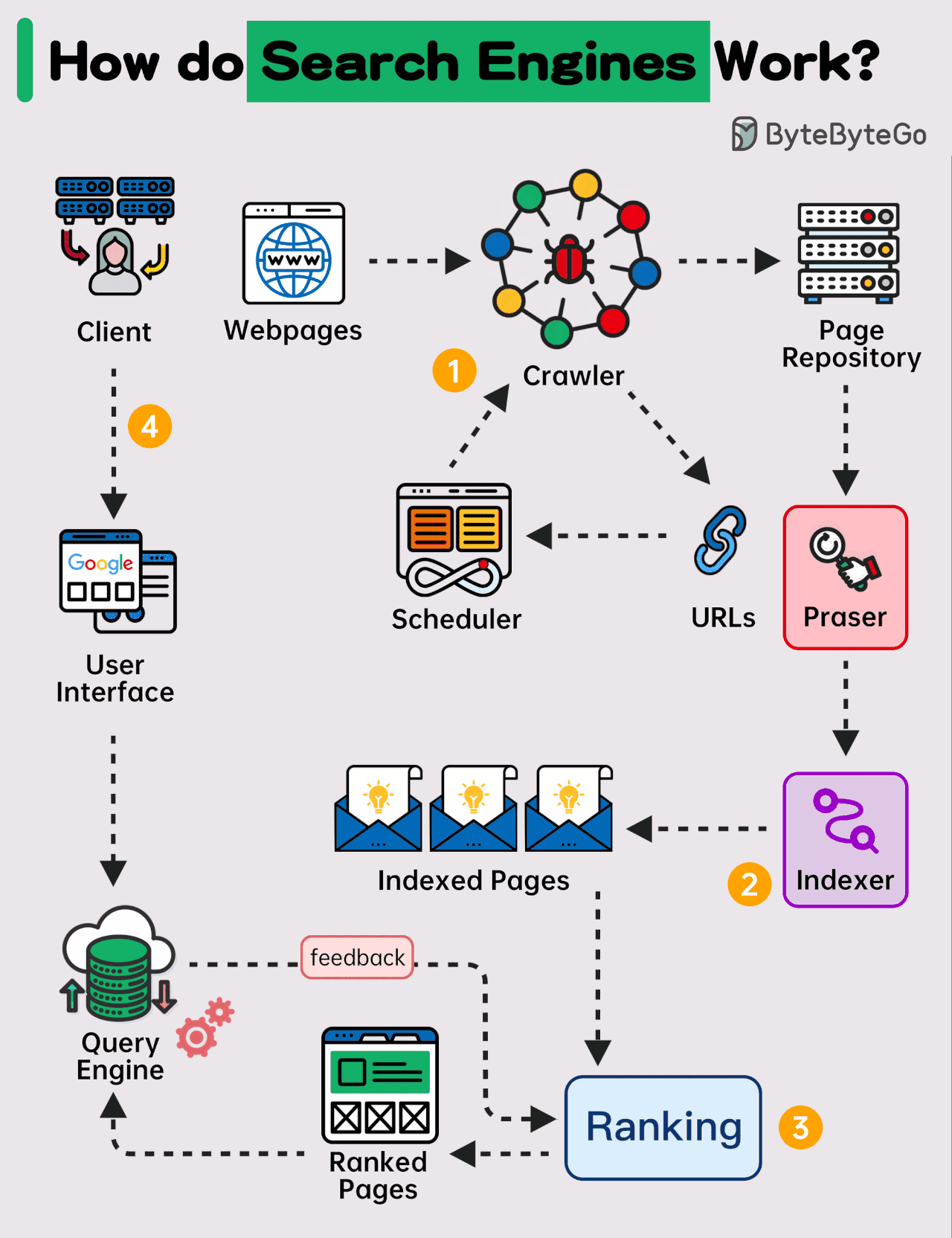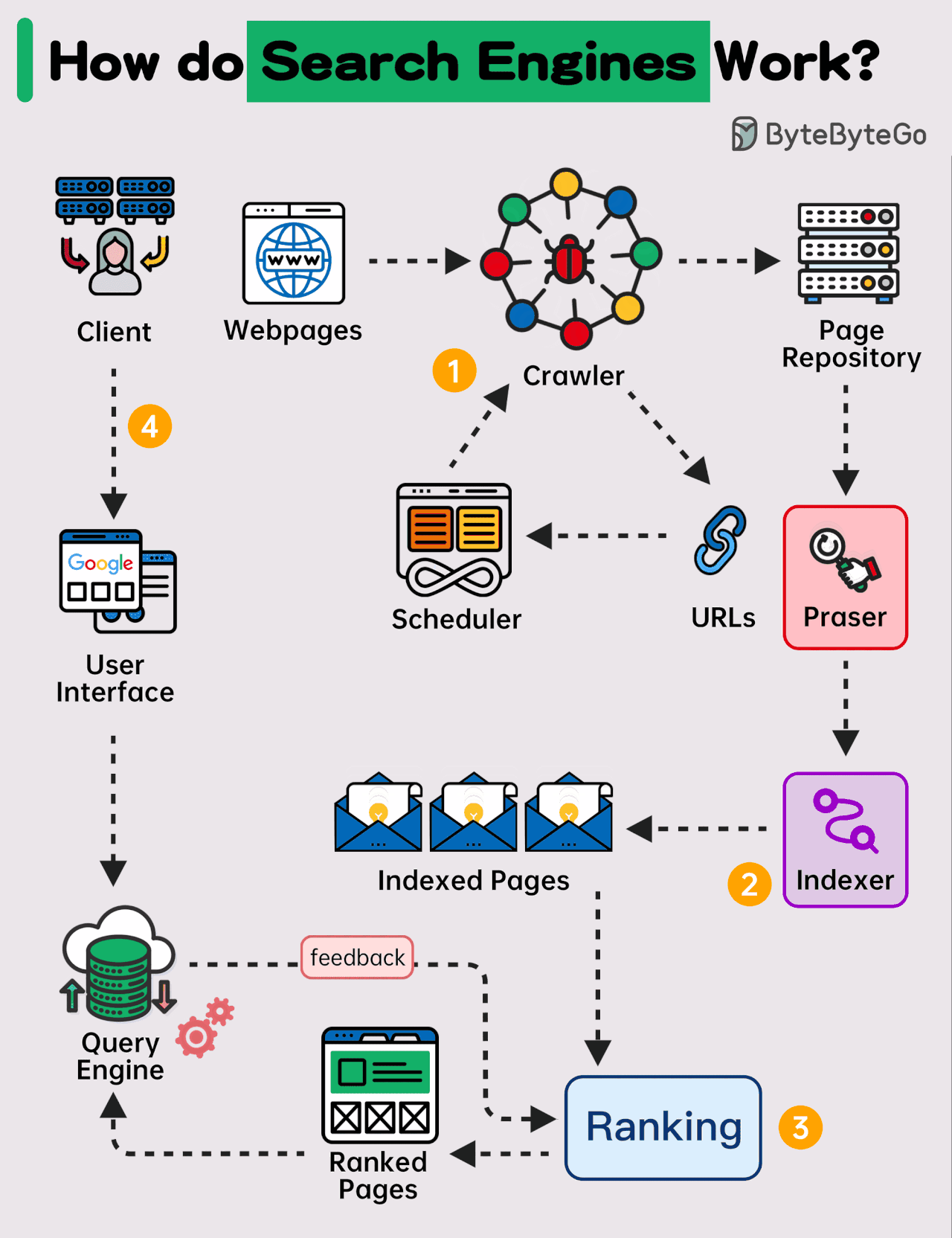
1. Crawling.
Search engines use automated programs known as crawlers or spiders to explore web pages all over the internet. These crawlers start with a list of URLs and follow links from one website to the next, discovering new pages along the way.
Bots (Crawlers):
Programs such as Googlebot crawl online pages, gathering content, and storing it in databases.
Frequency: Some pages are crawled more frequently than others, particularly if the material is regularly changed.
2. Indexing
When a web page is crawled, the search engine evaluates the material and stores it in an index, which is a massive database. During this step, the engine examines the content, which includes text, images, videos, and metadata, to determine what the page is about.
Content analysis is the process by which search engines read text, identify keywords, and take note of page structure.
Structured Data: Special tags (e.g., Schema Markup) enable search engines understand the context of specific material such as events, products, and reviews.
URL Storage: Pages are classified according to relevancy, context, and topic for easier retrieval later.
3. Ranking
When you search for something, the search engine employs sophisticated algorithms to prioritize the most relevant results. The ranking method selects which sites appear first based on a variety of criteria.
Relevance is how well a page’s content matches the search query.
Authority:
The trustworthiness of a page, as assessed by the number of other websites that link to it.
User Experience: Page load speed, mobile friendliness, and security (HTTPS) are all factors that influence rankings.
Engagement: User behavior, such as click-through rates and dwell time (the amount of time someone spends on a page), can influence rankings.
4. Retrieving Results
When a search query is entered, the search engine returns the most relevant results from its index. The results appear on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
Featured Snippets:
Some queries produce results directly on the search page (for example, definitions, calculations, or summaries).
Organic Results: These are unpaid results ranked by relevance and other criteria.
sponsored Results: Search engines such as Google display sponsored adverts (commonly labeled “Ads”) at the top or bottom of the SERP.
5. Algorithms
Search engines utilize complicated algorithms that are regularly updated. These algorithms consider several aspects to ensure that the user receives the most accurate and relevant results. Some things that influence these algorithms are:
Keywords:
The use of search terms in the title, headings, and body of the article.
Freshness: Recently updated material may be favored for specific queries.
Context and Intent: Search engines attempt to determine the intent of a query (informational, transactional, or navigational) in order to provide the best results.
6. Personalization
Search results may vary depending on the user’s location, search history, and preferences. Search engines may use cookies and other data to tailor results and increase relevance.
You can also read this Article from Linkdin:
How does a search engine and results?
if you like this article. Please do read this as well.

[…] How do Search Engines really Work […]